An Evaluation of Diabetes Ameliorating Capacity of Terminalia bellerica Ethanolic Extract on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rat Including Safety Profile Study.
Md Rafat Tahsin, Bushratul Jannat, Amira mostafa, Fahima Akhter Purni, Sanzida Khondoker, Samia Islam, Amena Alam Shanta, Sadia Afrin, Quazi Yousuf Asadullah, Md. Shah Amran
DOI10.36648/2572-5432.6.1.33
1Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, North South University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
2Department of Pharmacy, University of Asia Pacific, Dhaka, Bangladesh
3Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
4Department of Pharmacy, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
- Corresponding Author:
- Md Rafat Tahsin
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences
North South University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Tel: 8801704592755
E-mail: whitefang229@gmail.com
Received Date: December 19, 2020; Accepted Date: January 15, 2021; Published Date: January 22, 2021
Citation: Tahsin MdR, Jannat B, Mostafa A, Purni FA, Khondoker S, et al. An Evaluation of Diabetes Ameliorating Capacity of Terminalia bellerica Ethanolic Extract on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rat Including Safety Profile Study. J Clin Mol Endocrinol. 2021, 6:1.33. doi:10.36648/2572-5432.6.1.33
Copyright: © 2021 Tahsin MdR, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Diabetes is one of the world’s most widespread diseases. It is a chronic, metabolic condition and to treat this condition; plant extracted products are used. Plants are multifarious sources of different medicinal compounds that can be used to improve diabetes. The fruit of T. bellerica (commonly known as ‘Bohera’) is used for this purpose. Our present investigation was designed to investigate the hypoglycemic effect, lipid profile and safety profile and thus, monitored an ethanolic extract of T. bellerica fruit in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. In rats, diabetes was induced by intraperitoneal alloxan injection at a dose of 150 mg/kg body weight, and T. bellerica fruit extract was fed to the rats at a dose of 750 mg/kg. Blood glucose levels, lipid profile, and safety profile were assessed by measuring serum cholesterol, free fatty acids, phospholipids and triglycerides, SGOT, SGPT and creatinine levels in diabetic non-diabetic rats before and after extract administration. After evaluating the amount of blood glucose, the hypoglycemic efficacy was found to be equivalent to that of metformin (p> 0.05) given at a dose of 500 mg/kg. Lipid profile and safety profile were analyzed by measuring the levels of tissue cholesterol, free fatty acids, phospholipids and triglycerides, SGOT, SGPT and creatinine. It was found that both fruit extract of T. bellerica and metformin strengthened the diabetes-induced pathological condition. Besides, both fruit extract of T. bellerica and metformin did not substantially affect healthy individual rats’ normal physiological condition. So, it could be also be concluded that the fruit extract of i could be used as a successful alternative therapy for the treatment of diabetes.
Keywords
Terminalia bellerica; Diabetic Mallitus; Safety Profile; SGPT; SGOT; Creatinine
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a branch of metabolic disorder distinguished by chronic hyperglycemia [1] due to impaired insulin secretion [2-4]. Untreated diabetes results in some acute complications like ketoacidosis, hypoglycemia, nonketotic hyperosmolar coma [4], and chronic conditions including nephropathy, retinopathy, atherosclerosis, various organ failures, microangiopathy, and infections [5,6]. To control this complicated situation, a wide range of medication is prescribed to control blood glucose levels. The most commonly used antidiabetic drugs include insulin and its derivatives, thiazolidinediones (TZDs), glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, biguanides, sulfonylureas, amylin analogues and glucosidase inhibitor, and this range is widening day by day [7-10]. The conventional antidiabetic drugs have some adverse reactions. The most common side effect is the urinary tract infection. The glucose increases in the urine, and the infection occurring by bacteria mainly associated with diabetes. Hypotension occurs due to intravascular volume contraction, hyperkalemia, ketoacidosis, the risk of bone fractures, dehydration [11]. Some medicinal plants are used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. The bark of Acacia Arabica [12], seed of Boerhaavia diffusa [13], the fruit of Capsicum annuum [14], and the fruit of Coccinia indica [15] and so on are used.
The scientific name of bohera is Terminalia bellerica. It grows wildly throughout the Indian Subcontinent, Srilanka, and South East Asia; an elevation up to 1200 meters with extended etiological diversity can be found [16]. Mainly it is used in antibacterial drugs, but nowadays, it has been used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus [17].
It is as such a tree that is deciduous in nature and possesses a supported trunk, a dense brownish-gray bark including depthless longitudinal fissures, accomplishing a height of within 30 to 20 meters. The leaves are jammed around the edges of the branches, alternately arranged, margins entire, elliptic to elliptic obovate, rounded tip or subacute, midrib prominent, pubescent when young and becoming glabrous with maturity. The flowers hold an unpleasant odor and are fade greenish-yellow in color and produced in axillary spikes bigger than the petioles but shorter than leaves. The fruit come ovoid grey drupes, unclearly 5-angled, narrowed into a very tiny stalk [18-21].
It contains several phytochemical constituents such as glucoside (bellericanin) [22], gallo-tannic acid, coloring matter, resins and a greenish-yellow oil [23], ellagic acid, gallic acid, lignans (termilignan and thannilignan), 7- hydroxy 3’4’ (methylenedioxy) flavone and anolignan B [24], tannins, ethyl gallate, galloyl glucose and chebulagic acid, phyllemblin, β-sitosterol, mannitol, glucose, fructose and rhamnose [18,25].
Different parts of Terminalia bellerica have been recognized as capable of inducing diverse pharmacological response for example- immunological activity[24], β-lactamase inhibitor activity [26], immune response In vitro [24], wound healing activity [27], analgesic activity, antihypertensive effect [28], Anti-diarrheal activity [29], anti-salmonella activity [30], anti-microbial activity [31], antimicrobial and toxicity studies [32], antimutagenic activity [33], antipyretic activity [34], hepatoprotective activity [35], antithrombotic and thrombolytic activity [36], anti-spasmodic and bronchodilatory properties [37], antibiofilm activity [38], acute and sub-acute toxicities [39], antiulcer activity [40], antioxidant activity [23], anticancer activity [41] etc.
In this experimental investigation, our principal aim was to examine the antidiabetic and hypoglycemic effect of Terminalia bellerica in diabetic rodents.
Method and Materials
Chemicals
Metformin, an antidiabetic drug, was obtained from Square Pharmaceuticals Limited, Salgaria, Pabna, Bangladesh, and an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API). Alloxan was brought from Sigma Aldrich, Germany. SGPT, SGOT and Creatinine measurement kits were purchased from Plasmatic Laboratory Product Ltd. Humalyzer 3000 (Semi-Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyzer derived from Medigroup Asia limited, Combodia) was used to assess several blood parameter parameters, the glucometer Alere GI of Alere Inc, the USA was obtained from Shahbag, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Extraction Procedure
The fruits of Terminalia bellerica Roxb were obtained from Botanical Garden, Mirpur and Dhaka. Fruits were washed with distilled water and then dried less than 45°C for 21 days, and then the properly dried fruits were crushed into powder. Next, the dry powder was shocked in 95% ethanol at a ratio of 1: 6 (Powder: Solvent) and kept for 7 days with occasional vigorous shaking. The same procedure was done thrice. After that, the extract was made to evaporate using Evaporator. The extract was then gathered. The yield of the extract was 12.4% (Modified) [42].
Experimental Design and Animal Handling
Healthy adult male Wistar rats (120-140 gm) were assembled from the Department of Pharmacy of Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Bangladesh and held at the Institute of Nutrition & Food Science, University of Dhaka at 25°C temperature and a 12±1 h light/dark cycle was strictly controlled. Standard pellet diet and water were provided (ad libitum) to the animals. The rats were kept there for acclimatization before starting the analysis. After that, the body weight of each rat was determined; animals were divided into 6 groups. The rodent was equally distributed according to its body weight, and each group included 5 rats.
Group 1: Negative Control.
Group 2: Positive Control.
Group 3: Alloxan induced animals treated with metformin, 200 mg/kg [43].
Group 4: Alloxan induced animals treated with the extract of Terminalia bellerica, 750 mg/kg.
Group 5: Non-diabetic rats treated with 200 mg/kg metformin [43].
Group 6: Non-diabetic rats receiving the extract of Terminalia bellerica, 750 mg/kg.
The rats were treated without persuading diabetes in the first two weeks with their respective specimens. Alloxan, a chemical agent, was then injected intraperitoneally into all rats belonging to groups 2, 3 and 4 at a dose 150 mg/kg [44,45]. These rats’ blood glucose levels were tested to see whether or not, after three days, they were affected by diabetes. The negative control group and alloxan injected positive control group was held untreated, where treatment with drugs and extracts was started in animals in groups 3, 5 and 4, 6, respectively. Forty-two days of treatment continued, and blood glucose levels were tested thrice in a week. Then, drug and plant extract doses were administered orally.
Statistical Analysis
The findings were expressed as mean ±SD for all study parameters belonging to different groups. “One Way Anova Test of SPSS 16” software was used to evaluate intra-group and inter-group discrepancies in outcomes to assess the statistical significance. The statistical significance level was set at a ‘p’ value of p>0.05. In terms of outcomes, the intragroup difference was considered statistically important when the ‘p’ value was found at 0.05.
Results
Change in body weights
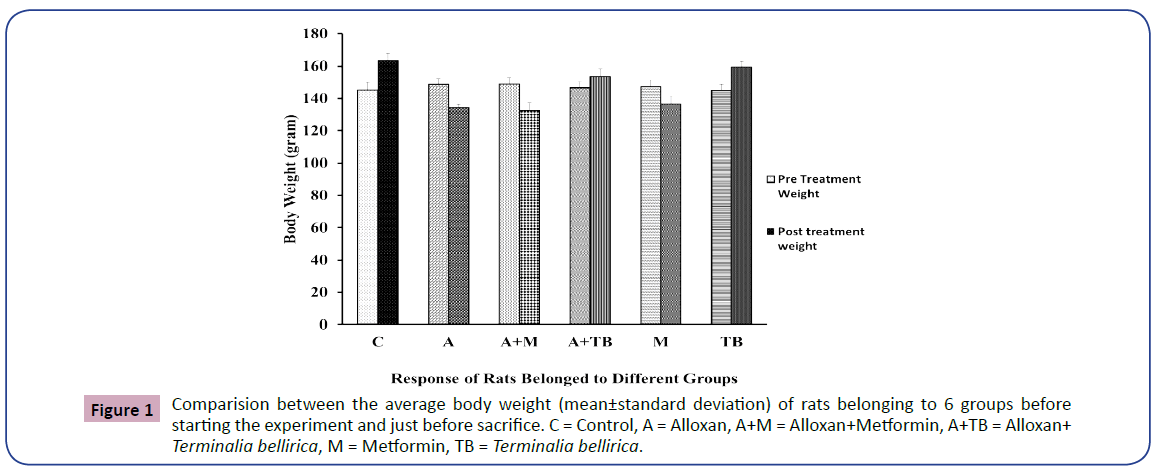
The pre-treatment & post treatment Body weight of rats belonged to different group is shown in below in Figure 1.
Change in blood glucose level
The blood glucose level (mg/dl) of all test group from day 1 to day 42 are expressing below as mentioned in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Blood glucose level of six groups from day zero to day forty two. The data were expressed as mean± standard deviation. * Expresses the significant change. C = Control, A = Alloxan, A+M = Alloxan+Metformin, A+ TB = Alloxan+Terminalia bellirica, M = Metformin, TB= Terminalia bellirica, * Expressing the significant change.
Safety Profile Study (Liver function test)
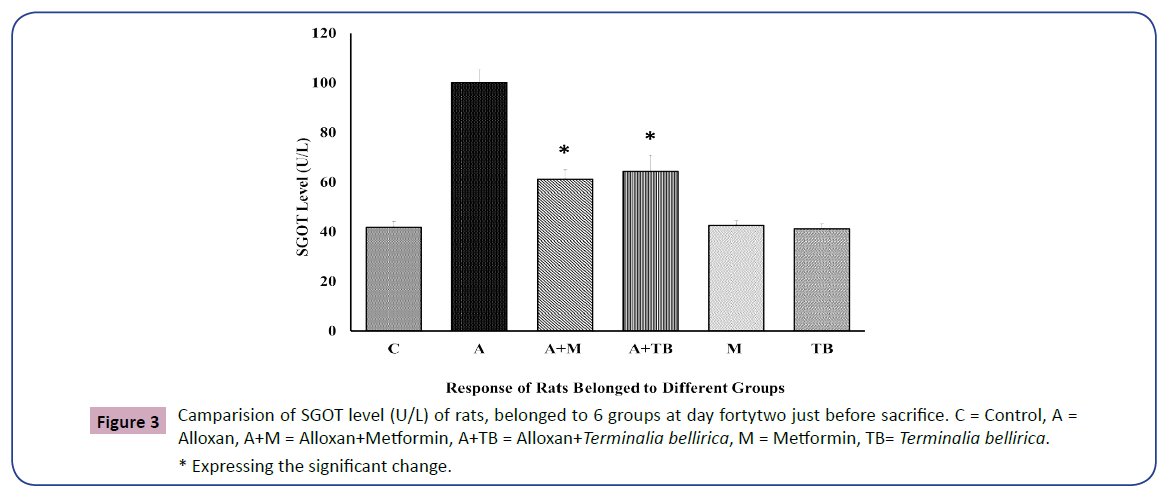
The SGOT level of all rats belonged to all 6 groups are denoting the condition of liver (Figure 3).
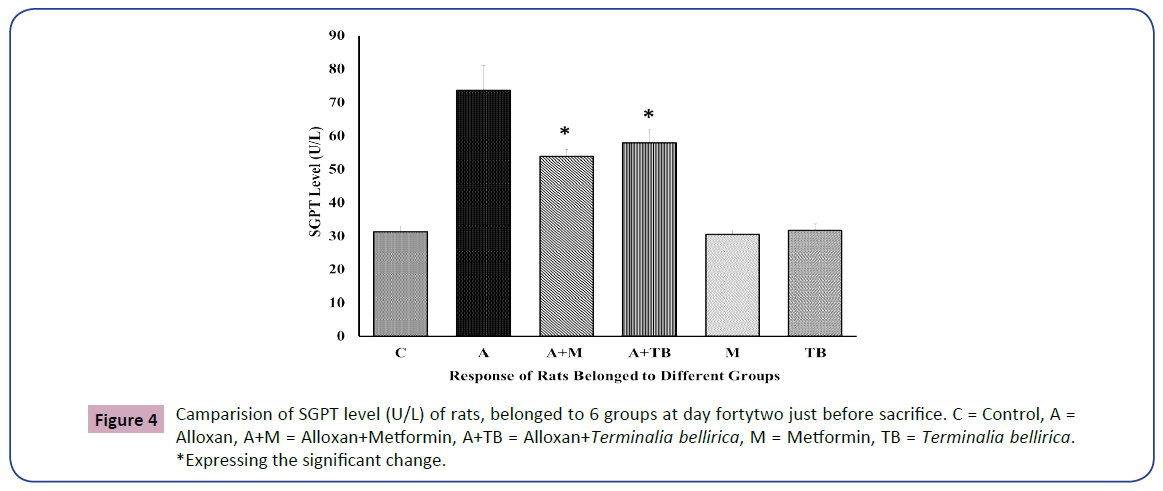
The level of SGPT of all rats belonged to 6 groups are expressing the condition of liver (Figure 4).
Safety Profile Study (Kidney functioning Test)
The below mentioned values regarding the level of Creatinine (md/dl) of rats belonged to all 6 groups as a requirement of measuring the kidney functioning test Figure 5).
Safety Profile Study (Lipid profile)
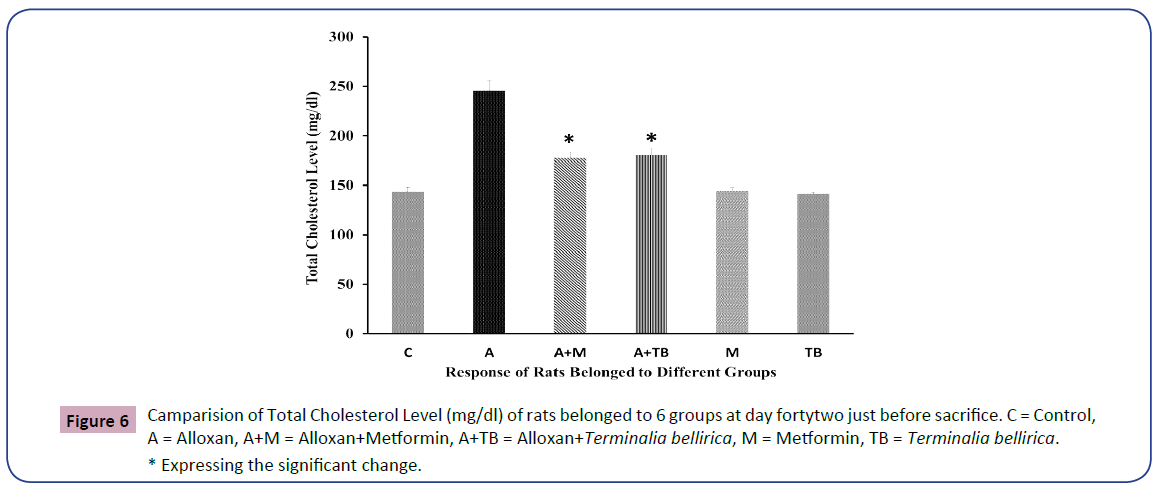
The Total Cholesterol level of rats belonged to all 6 groups is denoting the condition of Lipid profile (Figure 6).
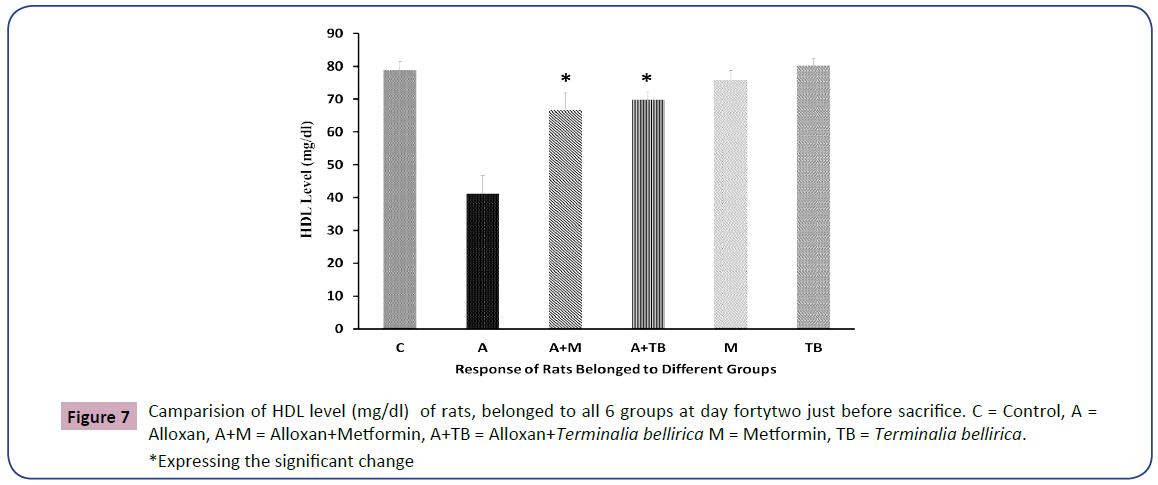
The level of HDL all rats belonged to 6 groups are expressing the condition of lipid profile (Figure 7).
Safety Profile Study (Lipid profile Test)
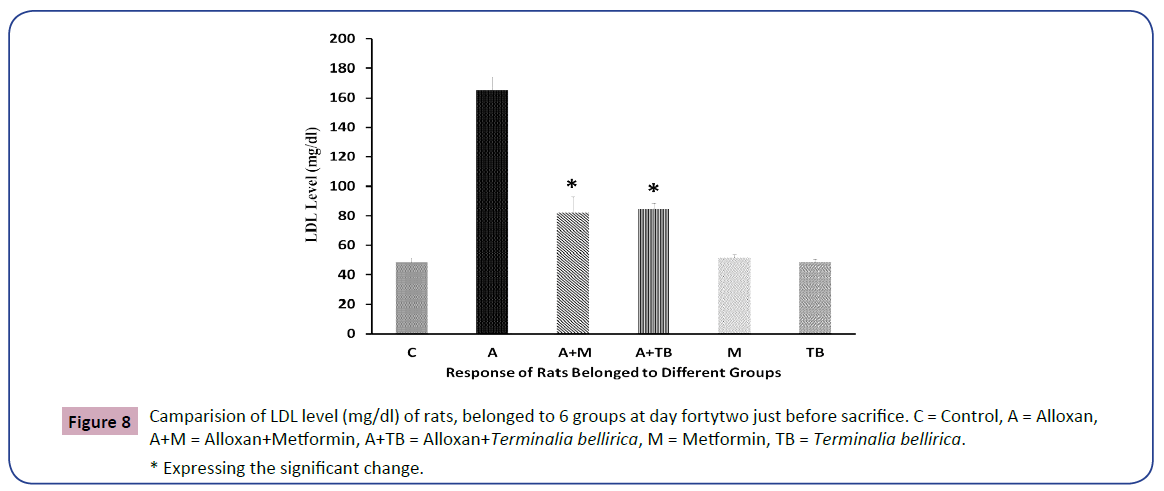
The below mention values regarding the level of LDL (md/dl) of rats belonged to 6 group as a requirement of measuring the lipid profile (Figure 8).
Safety Profile Study (Lipid profile Test)
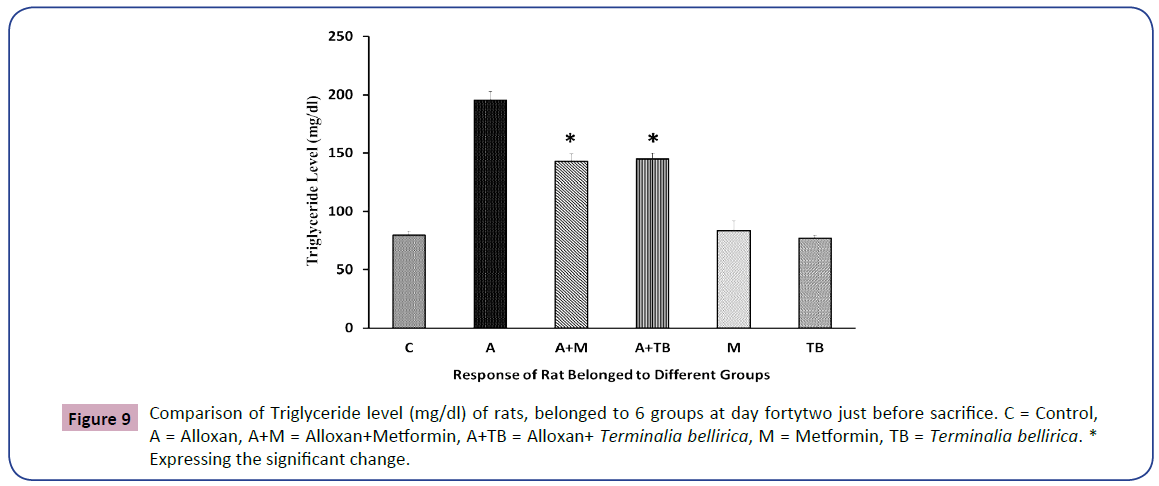
The level of Triglyceride level (mg/dl) of all rats belonged to 6 groups are expressing the lipid profile (Figure 9).
Discussion
Body weight measurement
Groups 2 and 3 had almost equal body weight, but significantly higher body weight was found in rats belonging to group 4 compared to groups 2 and 3. The control group and group 6 displayed a significantly identical but significant decrease in body weight, as was also detected in group 5. When correlated to the diabetic control group, with the metformin and extract-treated group, a significant reduction was observed in the metformintreated group. Because metformin has been reported to cause weight loss [46]. But the extract-treated group is nearly identical to the control group. However, both metformin and the extracttreated group were fed correspondingly as the control group. In the case of plant Costus pictus, a similar consequence was noticed [47].
Blood Sugar level
Group 2 appeared higher blood glucose levels than group 3 and group 4. Thus, contrasted to group 2, a significant decrease was observed in group 3 and group 4. Blood glucose levels in group 1 rats were encountered to be normal. The elevated blood glucose level was significantly reduced in the same pattern in the metformin and the extract-treated group as in the control group. It was precedently denoted that both metformin and plant Terminalia bellirica did not cause hypoglycemia [48]. Furthermore, the reduction of blood glucose in the group treated with metformin was slightly higher than that of the group treated with extract, but it has no statistical significance. A resemblant outcome was observed in the case of plant Panicum maximum [49].
Lipid profile
In the existing study, we have recognized a notable increase in total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides levels in blood serum. Still, a significant decline in serum HDL levels was noticed in alloxan-induced diabetic rats than in group 3 and group 4. Total cholesterol, LDL, and triglyceride levels were nearly identical between groups 3 and 4 with null statistical significance. Again, the HDL level of group 3 revealed a little bit better condition than group 4 and significantly nullified. Whole lipid profiles were almost indistinguishable in the control group of normal healthy rats treated with Terminalia bellirica and metformin and were also statistically nullified. A consistent result was found in the case of the plant Sigesbeckia orientalis [5].
Liver functioning test
Group 2, which corresponds to alloxan-induced diabetes rats, displayed higher SGOT and SGPT levels than group 3 and group 4. So, a significant decline was found in group 3 and group 4 compared with group 2. The drug-treated group was a little better condition between the drug and extract-treated group, which occupies statistical significance. In addition, SGPT and SGOT levels were almost identical in the control group of normal healthy rats treated with Terminalia bellirica and metformin, along with no statistical significance. When group 3 and group 4 are compared with the control group, significant results are seen. Rats were given drugs and extracted in group 5 and group 6, but in group 3 and group 4, rats were given alloxan with drug and extract. It can be assumed that alloxan is responsible for the significant result, not for the plant itself. In the case of plant Ocimum sanctum, a similar result was found [50].
Kidney functioning test
Group 2, which considers alloxan-induced diabetes, reported higher creatinine levels in rats relative to group 3 and group 4. Thus, compared to group 2, a significant decrease was noted in group 3 and group 4. A marginally better situation between the drug and the extract-treated group was the drug-treated group, which exhibits statistical significance. Besides, in the control group of normal healthy rats treated with Terminalia bellerica [51] and metformin, creatinine serum concentration was found to be approximately uniform with no statistical significance. Significant differences are found when group 3 and group 4 are compared to the control group. In group 5 and group 6, rats were given drug and extract, but in group 3 and group 4, rats were given alloxan with drug and extract. Alloxan can be said to be responsible for the essential outcome, not for the plant itself. An identical result was found in the case of plant Murraya koenigii [52].
Conclusion
The above-discussed outcome may be presumed that the T. bellerica fruit extracts impart alike but slightly lower effect than metformin with null statistical significance. Additionally, it ameliorates the state of pathological parameters in diabetic rats like SGOT, SGPT and Creatinine and imparts an anti-diabetic effect. Furthermore, it is also noticed that these parameters remain unchanged when non-diabetic rats were fed with T. bellerica with a similar dose. Thus, we put an end to the research by saying that this herbal cure can be merged for disease management of diabetes mellitus.
References
- Goldenberg R, Punthakee Z. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes, prediabetes and metabolic syndrome. Canadian journal of diabetes. 2013 Apr 1;37:S8-11.
- Piero MN, Nzaro GM, Njagi JM. Diabetes mellitus-a devastating metabolic disorder. Asian journal of biomedical and pharmaceutical sciences. 2015 Jan 1;5(40):1.
- Rashid R, Ahmad H, Ahmed Z, Rashid F, Khalid N. Clinical investigation to modulate the effect of fenugreek polysaccharides on type-2 diabetes. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre. 2019 Jul 1;19:100194.
- Bastaki A. Diabetes mellitus and its treatment. International journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2005 Jan 1;13(3):111.
- Asmat U, Abad K, Ismail K. Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress—A concise review. Saudi pharmaceutical journal. 2016 Sep 1;24(5):547-53.
- Piero MN. Hypoglycemic effects of some Kenyan plants traditionally used in management of diabetes mellitus in eastern province (Doctoral dissertation, Msc thesis, Kenyatta University).
- Wolverton D, Blair MM. Fracture risk associated with common medications used in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy. 2017 Aug 1;74(15):1143-51.
- Bösenberg LH, Van Zyl DG. The mechanism of action of oral antidiabetic drugs: a review of recent literature. Journal of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa. 2008 Dec 1;13(3):80-8.
- Qaseem A, Humphrey LL, Sweet DE, Starkey M, Shekelle P. Oral pharmacologic treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Annals of internal medicine. 2012 Feb 7;156(3):218-31.
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes care. 2015 Jan 1;38(1):140-9.
- Gurnell M, Savage DB, Chatterjee VK, O’Rahilly S. The metabolic syndrome: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and its therapeutic modulation. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2003 Jun 1;88(6):2412-21.
- Yasir M, Jain P, Debajyoti D, Kharya MD. Hypoglycemic and antihyperglycemic effect of different extracts of acacia arabica lamk bark in normal and alloxan induced diabetic rats. International Journal of Phytomedicine. 2010 Apr 1;2(2).
- Nalamolu RK, Boini KM, Nammi S. Effect of chronic administration of Boerhaavia diffusa Linn. leaf extract on experimental diabetes in rats. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2004;3(1):305-9.
- KWON YI, Apostolidis E, Shetty K. Evaluation of pepper (Capsicum annuum) for management of diabetes and hypertension. Journal of Food Biochemistry. 2007 Jun;31(3):370-85.
- Gunjan M, Jana GK, Jha AK, Mishra U. Pharmacognostic and antihyperglycemic study of Coccinia indica. International journal of phytomedicine. 2010 Jan 1;2(1).
- Saraswathi Motamarri N, Karthikeyan M, Kannan M, Rajasekar S. Terminalia belerica Roxb.—A phytopharmacological review. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2012;3:96-9.
- Shaw JH. Causes and control of dental caries. New England Journal of Medicine. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):996-1004.
- Singh A, editor. Herbalism, phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology. CRC Press; 2011 Apr 11.
- Singh A. Medicinal plants of the world, Published by Mohan Primlani for Oxford and IBH Co. Pvt, New Delhi. 2006;26.
- Nadkarni KM. Indian Meteria Medica, Published by Ramdas Bhatkal for Popular Prakashan Pvt. Ltd. Mumbai. 2002;1:202-1205.
- Elizabeth L, Bupesh G, Susshmitha R. In Vitro antioxidant efficacy of Terminalia Bellirica seed extract against free radicals. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research. 2017 Nov 1.
- Zeeshan U, Barkat MQ, Mahmood HK. Phytochemical and antioxidant screening of Cassia angustifolia, Curcuma zedoaria, Embelia ribes, Piper nigrum, Rosa damascena, Terminalia belerica, Terminalia chebula, Zingiber officinale and their effect on stomach and liver. Matrix Sci. Pharma. 2018;2(2):15-20.
- Saraphanchotiwitthaya A, Sripalakit P, Ingkaninan K. Effects of Terminalia bellerica Roxb. methanolic extract on mouse immune response in vitro.
- Shaikh S, Lochan R, Kaul P, Tandon GD. Beta lactamase inhibitors from indigenous herbs and spices. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014;5:275-85
- Singh A, editor. Herbalism, phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology. CRC Press; 2011 Apr 11.
- Shaikh S, Lochan R, Kaul P, Tandon GD. Beta lactamase inhibitors from indigenous herbs and spices. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014;5:275-85.
- Saha PK, Patrab PH, Pradhan R, Radharaman Dey SD, Mandal TK. Effect of Terminalia belerica & Terminalia chebula on wound healing in induced dermal wounds in Rabbits. Pharmacology online. 2011;2:235-41.
- Khan AU, Gilani AH. Pharmacodynamic evaluation of Terminalia bellerica for its antihypertensive effect. Journal of food and drug analysis. 2008 May 1;16(3).
- Kumar B, Divakar K, Tiwari P, Salhan M, Goli D. Evaluation of anti-diarrhoeal effect of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of fruit pulp of Terminalia belerica in rats. Int J Drug Dev Res. 2010;2(4):769-9.
- Madani A, Jain SK. Anti-Salmonella activity of Terminalia belerica: in vitro and in vivo studies.
- Elizabeth KM. Antimicrobial activity ofTerminalia bellerica. Indian journal of clinical Biochemistry. 2005 Jul 1;20(2):150-3.
- Alam MB, Zahan R, Hasan M, Khan MM, Rahman MS, Chowdhury NS, Haque ME. Thank You, a good research antioxidant, antimicrobial and toxicity studies of the different fractions of fruits of Terminalia belerica Roxb. Global Journal of Pharmacology. 2011;5(1):07-17.
- Kaur S, Arora S, Kaur S, Kumar S. Bioassay-guided isolation of antimutagenic factors from fruits of Terminalia bellerica. Journal of environmental pathology, toxicology and oncology. 2003;22(1).
- Sharma US, Sharma UK, Singh A. Screening of Terminalia bellirica fruits extracts for its analgesic and antipyretic activities. Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences. 2010 Jun;147(615):1-4.
- Jadon A, Bhadauria M, Shukla S. Protective effect of Terminalia belerica Roxb. and gallic acid against carbon tetrachloride induced damage in albino rats. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2007 Jan 19;109(2):214-8.
- Ansari AV, Siddiqui HH, Singh SP. Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic activity of Terminalia belerica fruit extracts. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical science. 2012 Apr;3(2):471.
- Gilani AH, Khan AU, Ali T, Ajmal S. Mechanisms underlying the antispasmodic and bronchodilatory properties of Terminalia bellerica fruit. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2008 Mar 28;116(3):528-38.
- Yadav S, Singh S, Sharma P, Thapliyal A, Gupta V. Antibiofilm formation activity of Terminalia bellerica plant extract against clinical isolates of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus: implication in oral hygiene. Int J Pharm Biol Arch. 2012;3(4):816-21.
- Thanabhorn S, Jaijoy K, Thamaree S, Ingkaninan K. Acute and subacute toxicities of the ethanol extract from the fruits of Terminaliabelerica (Gaertn) Roxb. J Pharm Sci. 2006;33(1-4):23-30.
- Choudhary GP. Anti-ulcer activity of the ethanolic extract of Terminalia belerica Roxb. Int J Pharm Chem Sci. 2012 Oct;1:1293-7.
- Pinmai K, Chunlaratthanabhorn S, Ngamkitidechakul C, Soonthornchareon N, Hahnvajanawong C. Synergistic growth inhibitory effects of Phyllanthus emblica and Terminalia bellerica extracts with conventional cytotoxic agents: doxorubicin and cisplatin against human hepatocellular carcinoma and lung cancer cells. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG. 2008 Mar 14;14(10):1491.
- Al-Amin MM, Uddin MM, Rizwan A, Islam MS. Effect of ethanol extract of Coccinia grandis Lin leaf on glucose and cholesterol lowering activity. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International. 2013 Aug 28:1070-8.
- Hassan Z, Yam MF, Ahmad M, Yusof AP. Antidiabetic properties and mechanism of action of Gynura procumbens water extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Molecules. 2010 Dec;15(12):9008-23.
- Yin P, Wang Y, Yang L, Sui J, Liu Y. Hypoglycemic effects in alloxan-induced diabetic rats of the phenolic extract from Mongolian Oak Cups enriched in ellagic acid, kaempferol and their derivatives. Molecules. 2018 May;23(5):1046.
- Sharma SB, Nasir A, Prabhu KM, Murthy PS, Dev G. Hypoglycaemic and hypolipidemic effect of ethanolic extract of seeds of Eugenia jambolana in alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2003 Apr 1;85(2-3):201-6.
- Seifarth C, Schehler B, Schneider HJ. Effectiveness of metformin on weight loss in non-diabetic individuals with obesity. Experimental and clinical endocrinology & diabetes. 2013 Jan;121(01):27-31.
- Jayasri MA, Gunasekaran S, Radha A, Mathew TL. Anti-diabetic effect of Costus pictus leaves in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Diabetes Metab. 2008;16(3):117-22.
- Rösen P, Wiernsperger NF. Metformin delays the manifestation of diabetes and vascular dysfunction in Goto–Kakizaki rats by reduction of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews. 2006 Jul;22(4):323-30.
- Antia BS, Okokon JE, Umoh EE, Udobang JA. Antidiabetic activity of ethanolic leaf extract of Panicum maximum. Int J Drug Dev Res. 2010;2(3):488-92.
- Khan MR, Islam MA, Hossain MS, Asadujjaman M, Wahed MI, Rahman BM, Anisuzzaman AS, Shaheen SM, Ahmed M. Antidiabetic effects of the different fractions of ethanolic extracts of Ocimum sanctum in normal and alloxan induced diabetic rats. Journal of Scientific Research. 2010;2(1):158-68.
- Arulselvan P, Senthilkumar GP, Sathish Kumar D, Subramanian S. Anti-diabetic effect of Murraya koenigii leaves on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Die Pharmazie-An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2006 Oct 1;61(10):874-7.
- Asif M, Saleem M, Yousaf S, Saadullah M, Zafar M, Khan RU, Yuchi A. Antidiabetic activity of aqueous extract of Sigesbeckia orientalis (St. Paul’s Wort) in alloxan-induced diabetes model. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2019;55.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences